Overview
The group covers all aspects of fundamental physics related to spin electronics by employing a wide range of theoretical approaches including ab initio, tight-binding, free electron and diffusive methods, combined with micromagnetic simulation approaches based on solution of Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert (LLG) equation. This allows explaining experimental observations, providing solutions for specific problems and predicting novel properties and phenomena guiding the experimental work to optimize spintronic nanostructures.
Research directions
Electronic structure and magnetic properties of materials from first principles
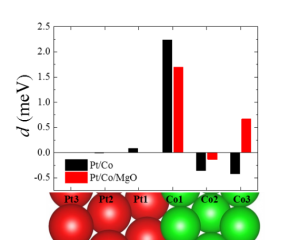
Ab initio calculations based on DFT are performed in order to provide insights into fundamental mechanisms of various spintronic phenomena, and to propose novel materials and their efficient combinations with required electronic structure and magnetic properties for optimal performance of spintronic devices.
Spin-dependent transport theories
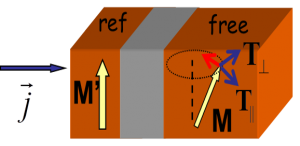
We employ tight-binding, free electron and diffusive approaches including Green function techniques in the framework of Keldysh and Kubo formalisms, in order to describe spin and charge transport properties in magnetic nanostructures with non-collinear magnetic moments in vertical, lateral and complex geometries.
Theoretical concepts for organic and graphene spintronics
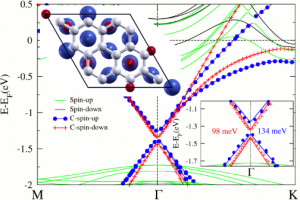
The goal of this topic is to harvest theoretically novel spin-dependent properties (e.g. proximity effects and defect induced magnetism etc.) in organic, graphene and related 2D materials based structures in the context of emerging field of graphene spintronics.
Micromagnetic modeling
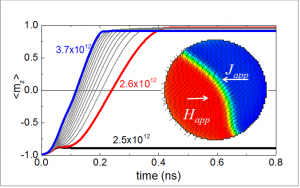
Magnetization dynamics (macrospin and micromagnetic) simulations under applied magnetic field and/or spin polarized currents are developed to address functionalities of spintronic devices (e.g. magnetization switching, synchronization and modulation for oscillators) in various geometries. Straightforward analytical models are developed to supplement fast and efficient understanding of the magnetization dynamics.
The team
Former members
Post-docs
- Ali HALLAL (2015-2019)
- Sergey NIKOLAEV (2015-2017)
- Debapriya CHAUDHURY (2016-2018)
- Cristian ORTIZ PAUYAC (2016-2017)
- Hongxin YANG (2013-2015)
PhD
- Daniel SOLIS LERMA (2016-2020)
- Paulo COELHO (with Magnetic Sensors Group, 2014-2017)
Internships
- Libor VOJACEK (2020)
- Brian CHARLES (with MRAM Group, 2016)
Projects
- ANR SpinSpike (2021-2024)
- ANR UFO (2021-2024)
- EU H2020 FET Project Flagship “Graphene” Core 3 (2020-2023)
- ANR MAGICVALLEY (2018-2021)
- ANR FEOrgSPIN (2018-2021)
- EU H2020 FET Project Flagship “Graphene” Core 2 (2018-2020)
- ANR JCJC MATEMAC-3D (2017-2020)
- EU H2020 ICT Project “SPICE” (2016-2020)
- EU H2020 ICT Project “GREAT” (2016-2019)
- ANR ELECSPIN (2016-2019)
- EU H2020 FET Project Flagship “Graphene” Core 1 (2016-2018)
- EU FET FP7 Project Flagship “Graphene” (2013-2016)
- EU M-ERA.NET HEUMEM supported via ANR-DFG (2014-2017)
- UGA Émergence et partenariat stratégique avec Western Digital (2015-2017)
- Samsung SGMI (2014-2017)
- ANR SOSPIN (2013-2016)
- ANR NMGEM (2010-2015)
- AGI14SMI15 AGIR (2014-2015)
Partners
- Transilvania University, Brasov, Romania
- IRIG/PHELIQS, Grenoble, France
- Institut Néel, Grenoble, France
- Unité Mixte Physique CNRS/Thalès, Palaiseau, France
- Laboratoire de Physique des Solides, Orsay, France
- Catalan Institute of Nanotechnology, Barcelona, Spain
- Institut Jean Lamour, Nancy, France
- Moscow Lomonosov State University, Moscow, Russia
- King Abdullah University of science and technology, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia
- University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, PR, USA
- Western Digital Corporation, CA, USA
- University of Bielefeld, Germany
- University of Kaiserslautern, Germany
- Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Dresden, Germany
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, USA
- ETH, Zurich, Switzerland
- NIMTE, Ningbo, China
Recent news
- Large-scale epitaxy of the van der Waals room-temperature ferromagnet Fe5GeTe2 (April 21st, 2022)
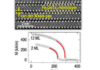
Van der Waals (vdW) layered magnets are promising materials to develop ultracompact and multifunctional spintronics devices. However, most of them are magnetic only at low temperature and are almost exclusively studied in the form of ... - Designing magnetic memory with improved retention and writability (April 08th, 2022)
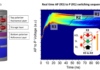
Magnetic Random Access Memory recently started to be commercialized by all main microelectronics factories. In MRAM, the information is coded via parallel or antiparallel magnetic configurations to represent ones and zeroes. The technology is intrinsically ... - Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya Interaction and Skyrmion States at 2D Materials/Co Interfaces (November 25th, 2021)
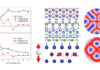
Significant Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction (DMI) and perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) at interfaces comprising hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) and cobalt (Co) remaining stable over a large range of Co film thickness are reported. Furthermore, it is demonstrated ... - A new spintronic memristive component for neuromorphic circuits (November 18th, 2021)
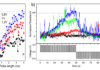
Neuromorphic computing is a bio-inspired technology which aims at mimicking the brain working principles. It can be used for fast and energy-efficient applications through the implementation of networks of artificial neurons and synapses. Artificial synapses ... - Introductory Course on Magnetic Random Access Memory (InMRAM 2021) (October 08th, 2021)

This introductory course aims at helping students, researchers and engineers having little or no background in magnetism to better understand the physics and working principles of this new class of magnetic memory called MRAMs (Magnetic ...















