Selected publications (2016 onwards)
Single-particle mass spectrometry with nanomechanical resonators (October 04th, 2018)
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an essential tool in a broad variety of fields, with good efficiency up to the kDa mass range (~10-21 g). We demonstrate here Nano-electro-mechanical systems mass spectroscopy (NEMS-MS) with arrays of individually addressed nanomechanical resonators, allowing for measurements in the MDa (~10−18 g) to GDa (~10−15 g) mass range. Monocrystalline silicon […]
Read moreHighly Efficient Spin-to-Charge Current Conversion in Strained HgTe Surface States Protected by a HgCdTe Layer (October 03rd, 2018)
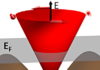
We report the observation of spin-to-charge current conversion in strained mercury telluride at room temperature, using spin pumping experiments. We show that a HgCdTe barrier can be used to protect the HgTe from direct contact with the ferromagnet, leading to very high conversion rates. Conventional spintronics is based upon the use of magnetic materials to […]
Read moreHigh speed and low area look-up table design based on MRAM memory (September 07th, 2018)
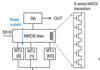
Continual growth in the size and functionality of FPGA over few years leads to an increasing interest in their use for high speed applications. However, the memory access speed limits the execution speed. The great amount of data affects the whole function. This work introduces a novel high speed and high-area efficiency MRAM based non-volatile […]
Read moreSub-10nm thermally stable Perpendicular Shape Anisotropy magnetic memory (August 24th, 2018)

A new concept of thermally stable and electrically switchable Spin Transfer Torque Magnetic Random Access Memory (STT-MRAM) scalable to diameter down to 4nm was proposed and demonstrated. By dramatically increasing the thickness of the storage layer, a bulk magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to the plane of the layers can be induced which dramatically improves the memory […]
Read moreNonlinear properties of pure spin conductors (June 21st, 2018)
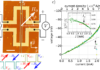
N. Thiery, A. Draveny, V. V. Naletov, L. Vila, J. P. Attané, C. Beigné, G. de Loubens, M. Viret, N. Beaulieu, J. Ben Youssef, V. E. Demidov, S. O. Demokritov, A. N. Slavin, V. S. Tiberkevich, A. Anane, P. Bortolotti, V. Cros, and O. Klein, Phys. Rev. B 97, 060409 (2018). N. Thiery, V. V. […]
Read moreDetection of Short-Waved Spin Waves in Individual Microscopic Spin-Wave Waveguides Using the Inverse Spin Hall Effect (June 21st, 2018)
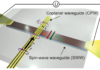
T. Brächer, M. Fabre, T. Meyer, T. Fischer, S. Auffret, O. Boulle, U. Ebels, P. Pirro, G. Gaudin, Nano Lett. 17, 7234 (2017) Detection of Short-Waved Spin Waves in Individual Microscopic Spin-Wave Waveguides Using the Inverse Spin Hall Effect We report on the wave-vector independent detection of short-waved spin waves with wavelengths down to 150 nm […]
Read moreSpin Hall and Spin Swapping Torques in Diffusive Ferromagnets (May 30th, 2018)
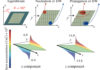
A complete set of the generalized drift-diffusion equations for a coupled charge and spin dynamics in ferromagnets in the presence of extrinsic spin-orbit coupling is derived from the quantum kinetic approach, covering major transport phenomena, such as the spin and anomalous Hall effects, spin swapping, spin precession, and relaxation processes. It is argued that the […]
Read moreChapter — Magnetic nanowires and nanotubes (April 14th, 2018)

Michal Stano, Olivier Fruchart, Magnetic nanowires and nanotubes, pp.155-267, in Handbook of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 27, E. Brück Ed (2018). DOI: 10.1016/bs.hmm.2018.08.002 We propose a review of the current knowledge about the synthesis, magnetic properties and applications of magnetic cylindrical nanowires and nanotubes. By nano we consider diameters reasonably smaller than a micrometer. At […]
Read moreEditor – Topical issue in MRS bulletin: Advanced memory—Materials for a new era of information technology (April 10th, 2018)

Bernard Dieny (from Spintec) and Cheol Seong Hwang are Guest Editors for a topical issue of the MRS Bulletin in May 2018, dedicated to Advanced memory—Materials for a new era of information technology. View online: DOI: 10.1557/mrs.2018.96 Material development has played a crucial role in modern civilization and information technology (IT). The importance of high-density […]
Read moreReview – Antiferromagnetic spintronics (March 12th, 2018)

V. Baltz, A. Manchon, M. Tsoi, T. Moriyama, T. Ono, and Y. Tserkovnyak, Rev. Mod. Phys. 90, 015005 (2018) Spintronics utilizing antiferromagnetic materials has potential for the next generation of applications and offers opportunities for new ideas. Ultimately, antiferromagnets could replace ferromagnets as the active spin-dependent element on which spintronic devices are based. Central to […]
Read more



