Sub-10nm thermally stable Perpendicular Shape Anisotropy STT-MRAM realized at SPINTEC (March 08th, 2018)
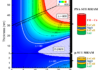
A team at SPINTEC in Grenoble has demonstrated thermally stable and electrically switchable Spin Transfer Torque MRAM (STT-MRAM) of diameter down to 4nm. Among the various technologies of non-volatile memories, STT-MRAM gathers a unique combination of assets: non-volatility, write speed (3-30ns), density (4Gbit demonstrated by Hynix/Toshiba), low consumption (a few tens of fJ/write), and very […]
Read moreEnhanced annealing stability and perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions using W layer (November 15th, 2017)
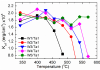
The stiffening of the perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction (pMTJ) stack resulting from the W insertion due to its very high melting temperature, is the key mechanism behind the extremely high thermal robustness. Thicker W layer in the W(t)/Ta 1 nm cap layer makes the storage electrode of pMTJ stack highly robust against annealing up to […]
Read moreSpin-Hall Voltage over a Large Length Scale in Bulk Germanium (July 20th, 2017)
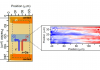
Germanium is one of the most appealing candidate for spintronic applications, thanks to its compatibility with the Si platform, the long electron spin lifetime and the optical properties matching the conventional telecommunication window. Electrical spin injection schemes have always been exploited to generate spin accumulations and pure spin currents in bulk Ge. Here, we use […]
Read moreNanotweezers and their remote actuation by magnetic fields (May 23rd, 2017)
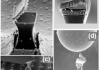
We have developed arrays of innovative magnetic nanotweezers or “nanojaws” on silicon wafers, by a top-down approach using the fabrication techniques of microelectronics. The mechanical manipulation of micro- and nanometric objects relies on constantly evolving techniques, which are of great interest to the life sciences and biotechnologies. Numerous biomedical studies, either fundamental or applied to […]
Read moreMillimeter-scale layered MoSe2 grown on sapphire and evidence for negative magnetoresistance (April 14th, 2017)
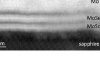
We have fabricated large-scale two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide (2D TMD) MoSe2, a promising candidate for electronics, valley-spintronics and optoelectronics, on insulating sapphire and have investigated its structural and transport properties. We have shown that the layered MoSe2 exhibits characteristics of a stoichiometric 2H-phase, a van der Waals epitaxy regarding the substrate and we have evidenced […]
Read moreEvidence for spin-to-charge conversion by Rashba coupling in metallic states at the Fe/Ge(111) interface (January 09th, 2017)
We have demonstrated the spin-to-charge interconversion by Rashba coupling at the interface between two light materials: iron and germanium which is compatible with today’s CMOS technology. This result constitutes the first step towards the fabrication of a spin transistor based on the spin-orbit coupling. The spin-orbit coupling, relating the electron spin and momentum, has long […]
Read moreA fluctuating magnetic order allows more spins to pass through an interface (February 26th, 2016)
Bringing a ferromagnetic layer to resonance creates non-equilibrium magnetization dynamics which generates a spin current. The spin current propagates from the ferromagnet into a neighboring layer if permitted by the interface. This is equivalent to saying that the air-flow generated by rotating the blades of a fan can propagate in a neighboring room if the […]
Read moreDes skyrmions magnétiques observés à température ambiante (February 09th, 2016)
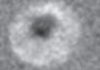
Ces structures magnétiques nanométriques ont été observées à températures ambiante dans des matériaux compatibles avec l’industrie électronique. Ces résultats font sauter un verrou important quant à l’utilisation des skyrmions comme vecteur d’information à l’échelle nanométrique dans nos ordinateurs.
Read more



